Introduction
Bitcoin mining is a crucial process that underpins the entire Bitcoin network. It’s not just about generating new coins; it involves validating transactions and securing the network against fraud. In this article, we will explore Bitcoin mining, detailing what it is, how it works, and why it matters. Understanding this process is essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency, investing, or the future of digital currency.
1. Understanding Bitcoin Mining
At its core, Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are created and transactions are verified. It involves powerful computers solving complex mathematical problems to validate and secure transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. Here’s a breakdown of how Bitcoin mining works:
1.1. The Blockchain
The blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions. Each block in the chain contains a list of recent transactions. When a miner successfully solves a mathematical puzzle, they add a new block to the chain. This process ensures that all transactions are securely recorded and cannot be altered.
1.2. Proof of Work
To add a block to the blockchain, miners must complete a process called “Proof of Work.” This requires significant computational power and energy consumption. The complexity of the puzzles ensures that it takes time and resources to mine new bitcoins, which helps maintain the integrity of the network.
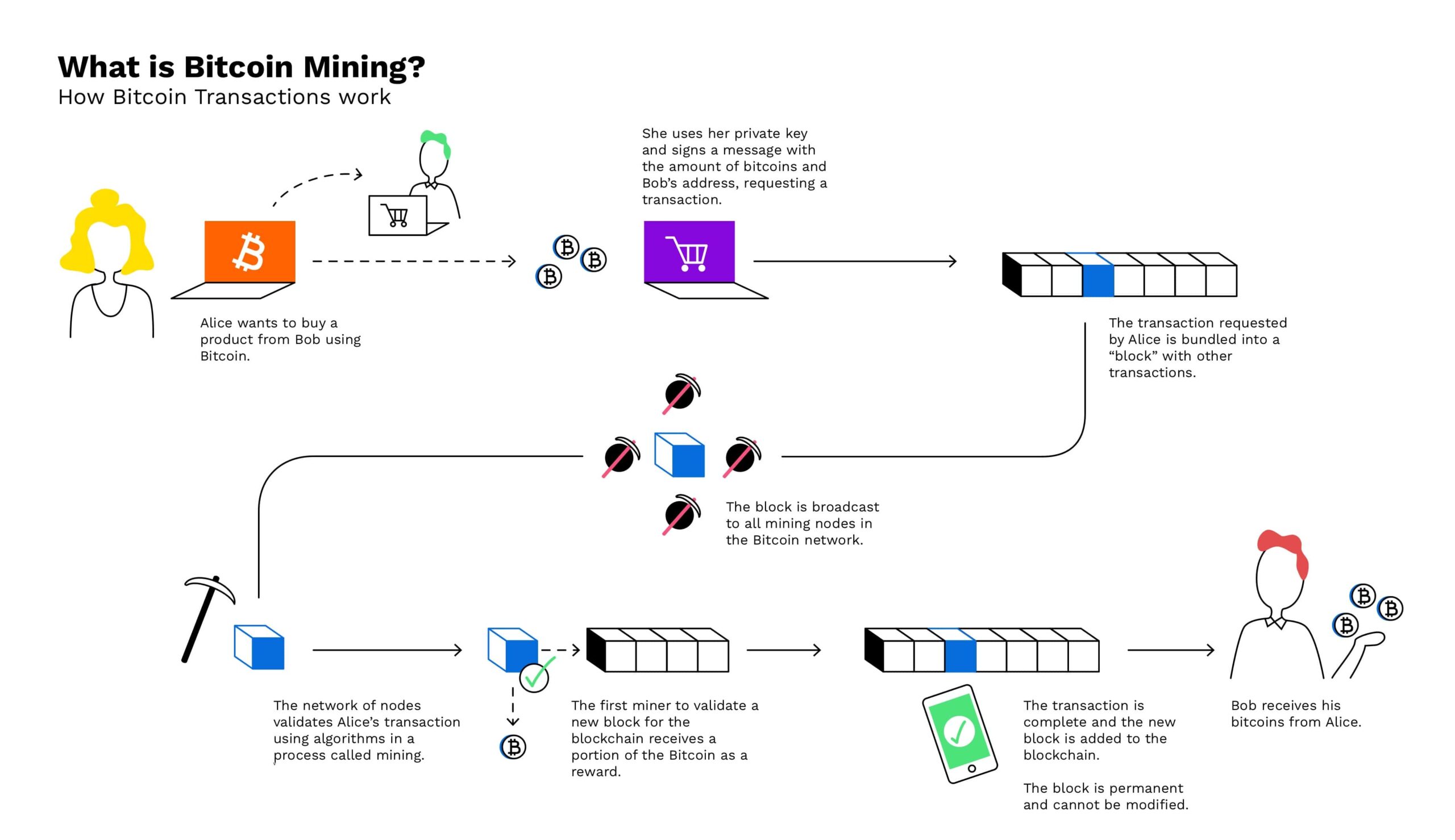
2. The Mining Process Explained
To truly understand Bitcoin mining, we must break down the process into several key steps:
2.1. Transaction Gathering
When users initiate transactions, these transactions are sent to a pool known as the mempool. Miners collect transactions from this pool to include in a new block.
2.2. Block Creation
Miners assemble transactions into a candidate block. Each block contains a unique header that includes a reference to the previous block, a timestamp, and a nonce (a random number used in the mining process).
2.3. Solving the Puzzle
Once a block is created, miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle. This puzzle is based on the SHA-256 hashing algorithm. Miners must find a nonce that, when combined with the block data, produces a hash that meets specific criteria (usually a certain number of leading zeros).
2.4. Block Verification
When a miner successfully solves the puzzle, they broadcast the new block to the network. Other miners and nodes verify the block’s validity, ensuring all transactions are legitimate and that the miner followed the rules of the network.
2.5. Rewards and Incentives
Once a block is verified, it is added to the blockchain. The miner who solved the puzzle receives a block reward, which currently consists of newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees from the transactions included in the block. This reward incentivizes miners to continue participating in the network.

3. The Economics of Bitcoin Mining
Understanding the economic factors that drive Bitcoin mining is essential for both miners and investors. Here are a few key points to consider:
3.1. Mining Difficulty
The mining difficulty adjusts approximately every two weeks to ensure that new blocks are added to the blockchain roughly every ten minutes. As more miners join the network, the difficulty increases. This adjustment helps regulate the supply of new bitcoins entering circulation.
3.2. Block Rewards
The block reward for miners started at 50 bitcoins and is halved approximately every four years in an event known as the “halving.” As of now, the reward is 6.25 bitcoins per block. This gradual reduction helps control inflation and ensures that the total supply of bitcoins is capped at 21 million.
3.3. Energy Costs
Bitcoin mining is energy-intensive due to the computational power required. Miners must consider electricity costs when calculating profitability. Many miners seek locations with low energy costs or utilize renewable energy sources to enhance profitability.

4. The Future of Bitcoin Mining
The landscape of Bitcoin mining is continually evolving. As technology advances and more miners enter the network, several trends are emerging:
4.1. Increased Regulation
Governments worldwide are beginning to regulate cryptocurrency mining to address environmental concerns and energy consumption. This regulation may impact how and where mining occurs.
4.2. Sustainable Practices
In response to criticism regarding its environmental impact, the Bitcoin mining community is exploring sustainable practices. Utilizing renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency are becoming priorities for many miners.
4.3. Mining Pools
Due to increasing difficulty, many miners join mining pools, where they combine their computational power to increase their chances of successfully mining blocks. Rewards are distributed among pool members based on their contribution to solving the puzzle.

5. Getting Started with Bitcoin Mining
If you’re considering entering the world of Bitcoin mining, here are some essential steps to get started:
5.1. Research Equipment
Investing in the right hardware is crucial. ASIC miners are specifically designed for Bitcoin mining and offer the best performance. Evaluate the cost of hardware, electricity consumption, and expected returns before making a purchase.
5.2. Select a Mining Pool
Joining a mining pool can enhance your chances of earning rewards. Research various pools and their fee structures to find one that aligns with your goals.
5.3. Set Up Your Wallet
Before you start mining, ensure you have a secure wallet to store your bitcoins. Choose between hot wallets (connected to the internet) and cold wallets (offline storage) based on your needs for accessibility and security.
Conclusion
In summary, Bitcoin mining is a vital process that maintains the integrity of the Bitcoin network while providing a means for individuals to earn new bitcoins. Understanding how Bitcoin mining works, the economic factors at play, and the future trends can empower you to navigate this exciting space. Whether you’re an aspiring miner or simply interested in cryptocurrency, grasping the fundamentals of Bitcoin mining is essential for success.

