Mining Difficulty Explained is a crucial concept for anyone involved in cryptocurrency mining. It directly impacts the ability of miners to successfully mine blocks and earn rewards. As more miners join the network, the competition increases, leading to changes in mining difficulty. Understanding this concept can help miners make informed decisions and optimize their mining strategies. In this article, we’ll delve into mining difficulty explained, discussing its importance, how it works, and what it means for miners in 2024.
1. What is Mining Difficulty?
Mining Difficulty Explained starts with the basics: what is mining difficulty? In the context of cryptocurrency mining, mining difficulty refers to the measure of how hard it is to find a new block in a blockchain. This metric is essential for maintaining a consistent block generation time within the network.
1.1 How Mining Difficulty Works
The mining process involves solving complex mathematical puzzles that require significant computational power. The more miners there are competing to solve these puzzles, the harder it becomes to find a block. The blockchain network adjusts the mining difficulty periodically to ensure that new blocks are added at a steady rate, typically every 10 minutes for Bitcoin.
1.2 Importance of Mining Difficulty
Understanding mining difficulty explained is vital for miners because it affects profitability and mining strategy. A higher difficulty means miners need more powerful hardware and resources to compete, while a lower difficulty allows for easier block discovery.
2. Factors Influencing Mining Difficulty
Several factors influence mining difficulty, making it essential for miners to stay informed. Here are some key elements:
2.1 Network Hash Rate
The network hash rate represents the total computational power being used by miners. When more miners join the network, the hash rate increases, leading to higher mining difficulty. Conversely, if miners leave the network, the hash rate decreases, resulting in lower difficulty.
2.2 Bitcoin Halving Events
Bitcoin halving events, which occur approximately every four years, cut the block reward miners receive in half. This event can affect mining difficulty as it impacts the incentive for miners to participate. Following a halving, if the network hash rate remains constant or increases, mining difficulty will likely rise.
2.3 Technological Advancements
Advancements in mining technology can also influence mining difficulty explained. As miners adopt more efficient hardware, the overall hash rate can increase, prompting adjustments to mining difficulty. Miners who stay updated on technology trends can gain a competitive advantage.
3. The Mining Difficulty Adjustment Algorithm
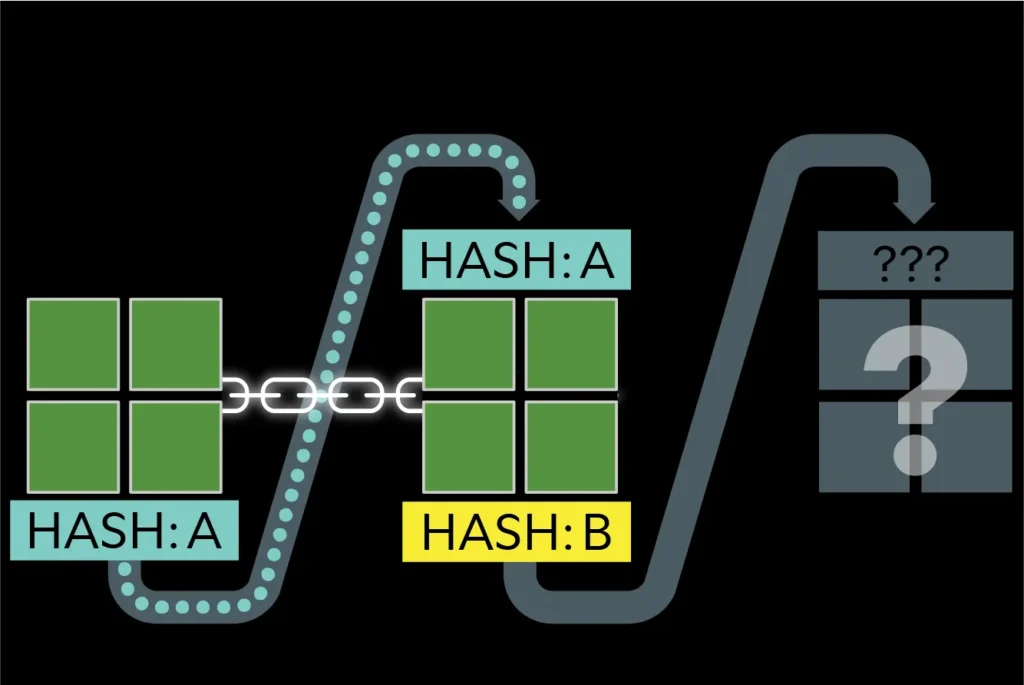
To maintain a stable block generation time, cryptocurrency networks implement a mining difficulty adjustment algorithm. This algorithm evaluates the time it took to mine the last set of blocks and adjusts the difficulty accordingly.
3.1 Bitcoin’s Difficulty Adjustment
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, uses a specific difficulty adjustment algorithm that evaluates the mining difficulty every 2016 blocks (approximately every two weeks). If the blocks were mined too quickly, the difficulty increases; if they took too long, the difficulty decreases. This process ensures that blocks are added at a consistent rate.
4. Impacts of Mining Difficulty on Miners
Understanding mining difficulty explained allows miners to comprehend its implications for their operations. Here are some of the most significant impacts:
4.1 Profitability
Higher mining difficulty means that miners need more resources to mine successfully. This increased competition can lead to reduced profitability, especially for those using less powerful hardware. Conversely, when difficulty decreases, miners may find it easier to turn a profit.
4.2 Hardware Requirements
As mining difficulty changes, miners may need to upgrade their hardware to remain competitive. Miners using older models may struggle to keep up with the increasing difficulty, leading to a potential need for investment in newer, more efficient mining rigs.
4.3 Strategic Adjustments
Miners must continually assess their strategies in response to changing mining difficulty. This includes considering factors such as electricity costs, hardware efficiency, and overall network conditions. Those who adapt quickly can capitalize on favorable conditions.
5. Future Trends in Mining Difficulty
As we look ahead to 2024 and beyond, several trends may impact mining difficulty explained:
5.1 Increasing Competition
The growing interest in cryptocurrency mining means that more individuals and organizations will likely enter the space. This influx can drive up mining difficulty, requiring miners to stay ahead of the curve with technology and strategy.
5.2 Regulatory Changes
Regulations surrounding cryptocurrency mining can influence mining difficulty. Stricter regulations may deter some miners, leading to a decrease in competition and a subsequent drop in difficulty.
5.3 Sustainable Mining Practices
As the environmental impact of mining becomes a more pressing concern, miners may shift towards more sustainable practices. This transition could affect the overall hash rate and, consequently, mining difficulty.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding mining difficulty explained is essential for anyone involved in cryptocurrency mining. It impacts profitability, hardware requirements, and overall strategy. As miners navigate the evolving landscape, staying informed about mining difficulty and its influencing factors will be crucial for success. By adapting to changes and embracing technology, miners can optimize their operations and thrive in the competitive world of cryptocurrency mining.